Machine learning based interpolation for regional water table w. Python and Scikit Learn - Tutorial
/Having a reasonable spatial distribution of the water table with few observation points is a challenge because the water table can't be above the surface. We wanted to develop a method where the computer learns not only about the position but also the surface to calculate the water table.
This is an applied example of water level interpolation based on a machine learning algorithm in Python with Scikit Learn. The code covers all steps from data compilation, regression formulation, accuracy testing and raster generation.
Tutorial
Code
Working on the data compilation
# import packages to compile the data
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np### creation of a dataframe for the neural network
wakeLoc = pd.read_csv('../Csv/WakeCoNC_slugtest_Wells.csv', usecols=[2,3,4,6])
wakeLoc = wakeLoc.set_index('well_name_short')
wakeLoc.head()| latitude_dd_nad1983 | longitude_dd_nad1983 | alt_mp_navd1988 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| well_name_short | |||
| CH-252 | 35.815336 | -78.925508 | 336.48 |
| WK-283 | 35.733056 | -78.675556 | 359.70 |
| WK-332 | 35.720833 | -78.500556 | 192.26 |
| WK-334 | 35.720833 | -78.500556 | 190.95 |
| WK-368 | 35.943000 | -78.684000 | 410.06 |
#add a value of hydraulic conductiviy. We read the hydraulic conductivities from another file and create a mean
wakeK = pd.read_csv('../Csv/WakeCoNC_slugtest_Analyses.csv',usecols=[1,6,19])
meanValues = wakeK.groupby('well_name_short')[['wl_static_dbls']].mean()
meanValues[:5]| wl_static_dbls | |
|---|---|
| well_name_short | |
| CH-252 | 41.2775 |
| WK-283 | 29.9800 |
| WK-332 | 16.8275 |
| WK-334 | 15.2825 |
| WK-368 | 121.0770 |
# apply the mean K to the original dataframe
wakeLoc['wlElev'] = -999.0
for index, row in wakeLoc.iterrows():
wakeLoc.loc[index,'wlElev'] = wakeLoc.loc[index,'alt_mp_navd1988'] - meanValues.loc[index,'wl_static_dbls']wakeLoc.to_csv('../Csv/wellDf.csv')
wakeLoc.tail()| latitude_dd_nad1983 | longitude_dd_nad1983 | alt_mp_navd1988 | wlElev | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| well_name_short | ||||
| WK-433 | 35.585893 | -78.678039 | 326.92 | 322.2050 |
| WK-434 | 35.585893 | -78.678039 | 328.43 | 301.4225 |
| WK-435 | 35.642404 | -78.825825 | 434.40 | 411.3175 |
| WK-436 | 35.695548 | -78.766925 | 435.93 | 412.4400 |
| WK-437 | 35.695548 | -78.766925 | 436.87 | 406.9200 |
Machine learning model construction
# import required packages
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression#define the two datasets
headValues = wakeLoc.iloc[:,3].values.reshape(-1,1) #because it is a single column
paramValues = wakeLoc.iloc[:,:3].values# Define the scaler
headScaler = StandardScaler().fit(headValues)
# Scale the train set
headValuesScaled = headScaler.transform(headValues)
headValuesScaled[:5]array([[-0.24772745],
[ 0.27174055],
[-2.05019526],
[-2.04665865],
[-0.34132725]])# Check scaler over head values
print(headValuesScaled.mean(axis=0))
print(headValuesScaled.std(axis=0))[-1.43675921e-16]
[1.]# Define the scaler
paramScaler = StandardScaler().fit(paramValues)# Scale the train set
paramValuesScaled = paramScaler.transform(paramValues)
paramValuesScaled[:5]array([[ 0.29272505, -2.01170002, -0.03127219],
[-0.35552737, -0.2333869 , 0.29555826],
[-0.45182133, 1.01166934, -2.06122429],
[-0.45182133, 1.01166934, -2.07966305],
[ 1.29853513, -0.29346549, 1.00439467]])# Check scaler over param values
print(paramValuesScaled.mean(axis=0))
print(paramValuesScaled.std(axis=0))[-4.61330320e-14 -7.14199941e-14 1.69798816e-16]
[1. 1. 1.]# Split over Train and Test
headTrain, headTest, paramTrain, paramTest = train_test_split(headValuesScaled, paramValuesScaled,
test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# Regressor
regr = MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,100,100),max_iter=50000).fit(paramTrain, headTrain)c:\Users\saulm\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\neural_network\_multilayer_perceptron.py:1650: DataConversionWarning: A column-vector y was passed when a 1d array was expected. Please change the shape of y to (n_samples, ), for example using ravel().
y = column_or_1d(y, warn=True)# Get predicted values for test array
headPredict = regr.predict(paramTest)# get the inverse for the test and predicted heads
headPredictedInversed = headScaler.inverse_transform(headPredict.reshape(-1,1))
headTestInversed = headScaler.inverse_transform(headTest.reshape(-1,1))# Create single subplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
# Scatter plot
ax.scatter(headTestInversed, headPredictedInversed, alpha=0.7, label='Data')
# Regression line
x_line = np.linspace(headValues.min(), headValues.max(), 100).reshape(-1, 1)
ax.plot(x_line, x_line, color='red', linewidth=2, label='Indentity Line')
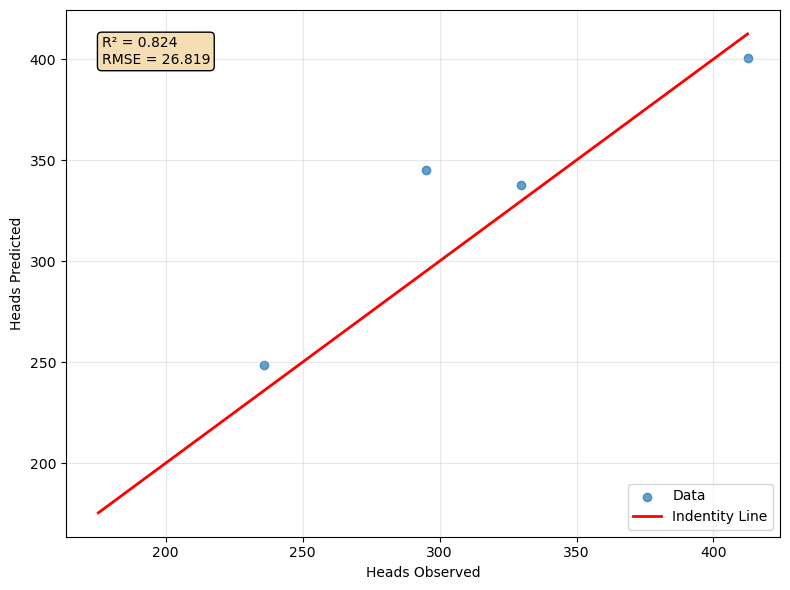
# Calculate metrics
r2 = r2_score(headTestInversed, headPredictedInversed)
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(headTestInversed, headPredictedInversed))
# Add metrics as text
metrics_text = f'R² = {r2:.3f}\nRMSE = {rmse:.3f}'
ax.text(0.05, 0.95, metrics_text, transform=ax.transAxes,
verticalalignment='top', bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='wheat'))
ax.set_xlabel('Heads Observed')
ax.set_ylabel('Heads Predicted')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Create the interpolated raster
import rasterio
from rasterio.plot import show#open dem and array
demFeet = rasterio.open('../Rst/areaDem_feet_NAD83_clip.tif')
demArray = demFeet.read(1)
demShape = demArray.shape
print(demShape)(1094, 1440)interpHeads = np.zeros(demShape)
paramTupleList = []
i = 0
for row in range(demShape[0]):
for col in range(demShape[1]):
x,y = demFeet.xy(row,col)
#print(x,y)
paramTuple = [y,x,demArray[row,col]] #lat, lon
#print(x,y,demArray[row,col])
#headPredict = v
#paramTupleScaled = paramScaler.transform([paramTuple])
paramTupleList.append(paramTuple)
if i % 400000 == 0:
print('processing %d cells, please be patient!'%i)
i+=1processing 0 cells, please be patient!
processing 400000 cells, please be patient!
processing 800000 cells, please be patient!
processing 1200000 cells, please be patient!paramTupleScaledList = paramScaler.transform(paramTupleList)demFeetMeta = demFeet.meta
demFeetMeta{'driver': 'GTiff',
'dtype': 'float32',
'nodata': -3.4028234663852886e+38,
'width': 1440,
'height': 1094,
'count': 1,
'crs': CRS.from_wkt('GEOGCS["NAD83",DATUM["North_American_Datum_1983",SPHEROID["GRS 1980",6378137,298.257222101004,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7019"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6269"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AXIS["Latitude",NORTH],AXIS["Longitude",EAST],AUTHORITY["EPSG","4269"]]'),
'transform': Affine(0.000277776805555558, 0.0, -78.833190499,
0.0, -0.0002777788464351009, 35.982082827)}interpHeadsList = regr.predict(paramTupleScaledList)
interpHeadsListInversed = headScaler.inverse_transform(interpHeadsList.reshape(-1,1))
interpHeadsListInversedarray([[345.69730345],
[348.84354167],
[347.86908141],
...,
[205.89600829],
[205.91801105],
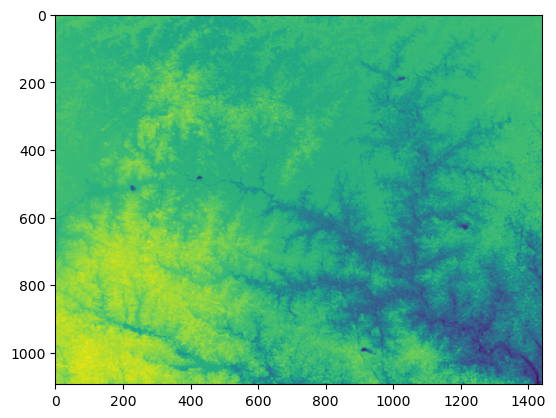
[208.86160631]])interpHeadsArray = interpHeadsListInversed.reshape(demShape)
plt.imshow(interpHeadsArray)<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x231937267b0>interpRaster = rasterio.open('../Rst/interpRaster.tif','w',**demFeetMeta)
interpRaster.write(interpHeadsArray,1)
interpRaster.close()Input data
You can download the input data from this link:
owncloud.hatarilabs.com/s/pyv9obJnyObR52m
Password: Hatarilabs