How to import and simulate a MODFLOW6 with Voronoi mesh model into Model Muse - Tutorial
/Did you know that you can import a Voronoi mesh MODFLOW 6 model created with mf6Voronoi into Model Muse. And you can not only import it, but also apply boundary conditions, solver parameters, review datasets, and simulate groundwater flow.
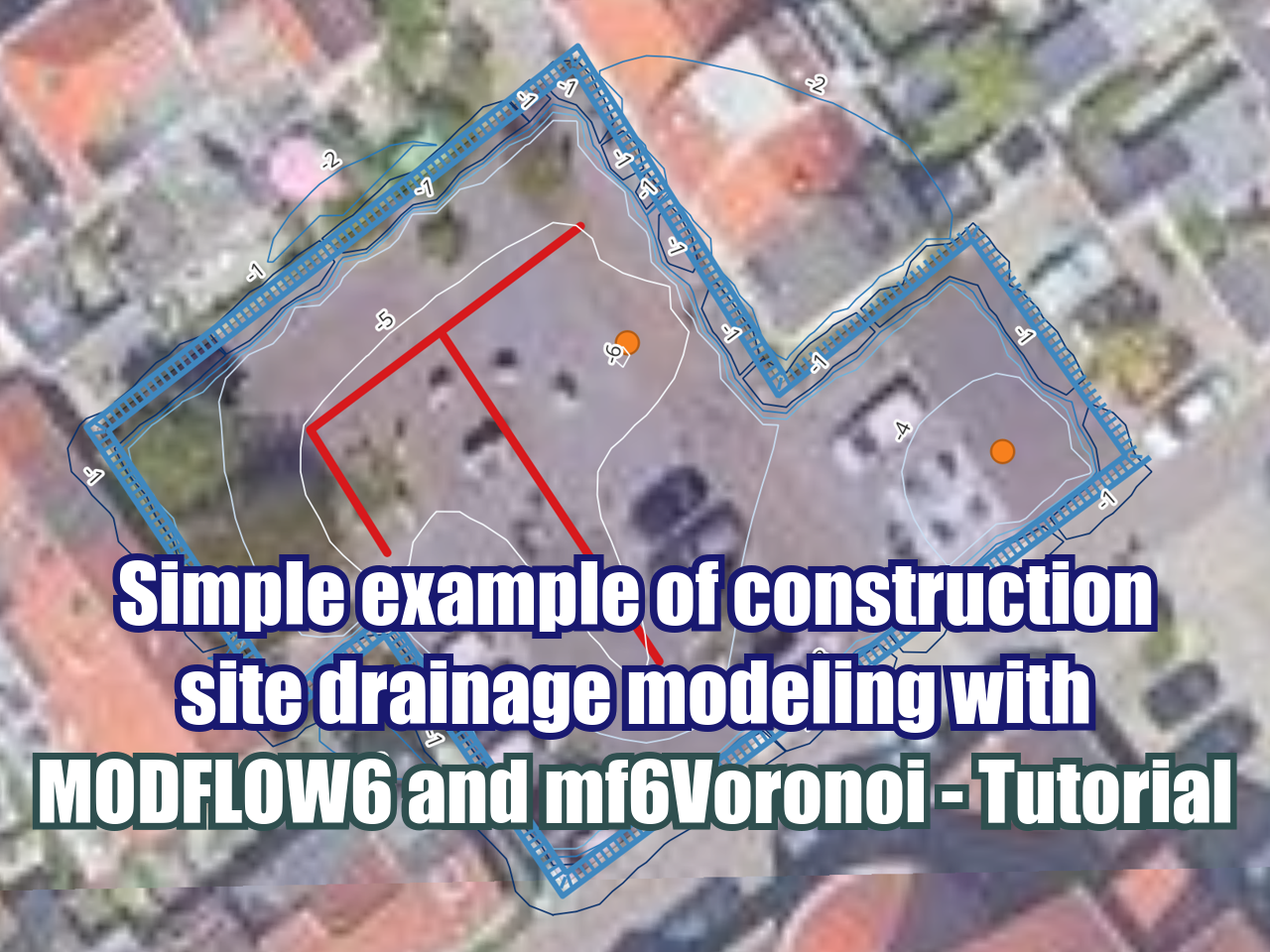
This tutorial shows a complete applied case for the import of the geometry and hydraulic parameters created with mf6Voronoi into Model Muse. The model is set up with boundary conditions, and simulated with different solver parameters.
Read More