Top 12 Best Open Source Software in Water Resources
/We have looked for different water resources free software, checked their documentation and analyzed their advantages and deficiencies to get this top 12.
Why are these software the best?
Because they are supported by big institutions and scientific communities.
Because they are always being updated.
Because documentation, tutorials and manuals are available.
Because there are a lot of research projects and publications related to them.
Why use free software?
First of all, because it is free. It does not have a monetary cost, does not require a license and can be used by anyone.
Another important reason is that their use improves the transparency of water resources and environmental evaluations since the results can be shared, supervised and observations can be made. In this way, software does not become an obstacle to understand and discuss impacts.
These software are (organized by categories):
Geographical Information Systems
1. QGIS
QGIS is the most popular GIS tool with an impressive trajectory and a vibrant community. It also even has a particular ecosystem of complements called “plugins”. QGIS is a completely open source alternative that reduces the cost barriers since it does not need a paid license and can be executed in any operative system.
Web: www.qgis.org
Vectorial layer of lines, polygons and points with QGIS
2. SAGA GIS
SAGA GIS is a GIS platform oriented to spatial analysis. SAGA GIS is a simple but powerful tool, with a big library focused on spatial analysis and characterization of basins. The interpolation options in SAGA GIS are better implemented than in other free and commercial software.
Web: www.saga-gis.org
Spatial analysis of an andean basin in SAGA GIS
River modeling
3. HEC-RAS
The numerical model HEC-RAS is developed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. This model uses the gradient and topography to evaluate the flow depth, velocities and flooded zones. It is also useful to calculate sediment transport and water temperature.
River scheme in HECRAS with cross sections.
4. iRIC
iRIC (International River Interface Cooperative) is a software developed with the purpose of offering a complete simulation environment of the riverbed and its results can be exported and used to analyze, mitigate and prevent disasters, through the visualization of the results of the river simulation.
Web: http://i-ric.org/en/
Visualization of flood related to a river modelled in iRIC
Hydrologic modeling
5. HEC-HMS
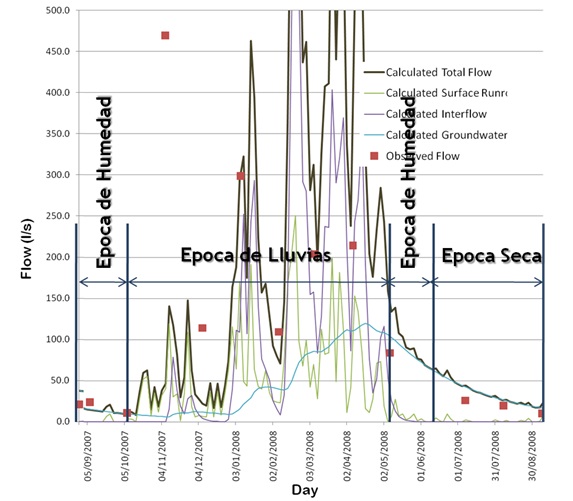
The Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) is designed to simulate the hydrologic processes in basins. The software includes traditional procedures of hydrologic analysis, such as infiltration events, unit hydrograms and routing. HEC-HMS also includes modules for evapotranspiration, snow melting and calculus of soil humidity.
Hydrologic model of an event in an andean basin
6. PRMS
The modeling code PRMS (Precipitation Runoff Modeling System) is a modular system of spatially distributed parameters, which represent the physical processes of a basin. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) to evaluate the effects of several combinations of geomorphology, type of soil, soil use, vegetation and climatic parameters in the hydrological response of a basin.
7. SWAT
SWAT is a tool to evaluate soil and water at a basin scale. It is focused in precipitation-runoff modeling and transport of water and solutes through surface flow. It predicts the impacts of soil management practices in water resources and sediments
Web: swat.tamu.edu
Hydrogeological modeling
8. MODFLOW
This code performs groundwater modeling based on finite differences developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS). It is capable of simulating groundwater 2D and 3D flux and simulate the principal physical processes related to the groundwater regime such as recharge, evapotranspiration, pumping, drainage, etc.
Numerical model of a 3D andean basin in MODFLOW
9. MT3DMS
The MT3DMS package is a mass transport model coupled to a flux model in MODFLOW. The MT3DMS code simulates advection, dispersion/diffusion and chemical reactions of adsorption/absorption of contaminants in groundwater.
Modeling of a contaminant plume in a mining waste dump
Computational fluid dynamics modeling
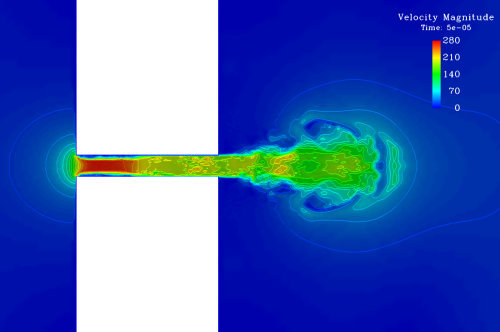
10. OpenFOAM
Pretty much any physical phenomenon associated to fluid dynamics can be represented with this software. The amount of packages incorporated and also its condition of an open source code make it useful to explore the possibilities of modeling several types of problems including the addition of a reactive model.
Web: www.openfoam.org
Scientific tools – programming
11. Python
This is the favorite code for scientific, water resources and environment analysis. It has several packages for different tools such as GIS, mathematical analysis and artificial intelligence.
If a complete tool for manipulation, processing and plotting of data is needed, Python – Scipy is an effective, versatile and free code solution.
Webs: www.python.org, www.scipy.org
Example of spatial and temporal analysis with Python - Scipy
12. R
R is a programming language for statistic calculations and graphics generation. It is easy to understand and makes it possible to make complicated analysis with just a few lines of code.
It is the best option to perform spatial analysis since it incorporates several interpolation options.
Web: r-project.org
Example of a regression with R